How to Actually Beat the S&P Long Term
Using systematic and rules based investing to improve your returns
Welcome back!!
This week we had veteran systematic trader Tim Fortier on the podcast.
With over 30 years of experience in fund management, technical analysis, and portfolio strategy, Tim shares key insights into building robust trading systems and adapting to market shifts.
If you want to take the emotion out of trading and transition to systematically building an edge through a rules-based approach, this is for you!
We dive into what’s at the heart of making money long-term in the markets, not just in a year, but how to create strategies that compound for decades.
I’ve learned a lot from Tim, here are my detailed notes from the conversation!
Develop Robust Back-Tested Strategies
Creating Robust, Rules-Based Trading Strategies
Avoid over-optimizing your trading models with excessive variables.
Keep strategies simple, relying on fundamental principles like supply and demand and price momentum.
Ensure strategies are valid across different market environments rather than just specific conditions.
Regularly test systems over long timeframes to confirm their consistency and adaptability.
Developing a Strong Backtesting Methodology
Ensure that backtesting data spans multiple economic cycles to gauge true performance.
Question the rationale behind selected factors and avoid data mining biases.
Identify whether a strategy performs well in specific macro environments or is universally applicable.
Use absolute momentum to filter out unfavorable market conditions and improve robustness.
Use Absolute Momentum for Risk Management
Compare an asset’s performance to its own historical performance before making trades.
Use absolute momentum to ensure that even strong relative performers are not declining overall.
Incorporate cash-like ETFs (SHV, SHY) into rankings to allow for defensive positioning during downturns.
Maintain exposure only when assets exhibit both positive absolute and relative momentum.
Don’t Settle for Dollar-Cost Averaging
Recognize the risks of passive investing in cap-weighted indices, which are highly concentrated in a few mega-cap stocks.
Consider equal-weighted indices or factor-based strategies for better diversification.
Actively manage exposure based on trend and momentum rather than relying solely on long-term holding.
Implement systematic rules to buy more aggressively in strong markets and scale back in weak markets.
Managing Drawdowns to Improve Risk-Adjusted Returns
Maintain symmetry between expected returns and maximum drawdowns.
Keep drawdowns within a tolerable range (e.g., a strategy with a 10-12% CAGR should have a max drawdown near that range).
Use historical analysis to ensure models can handle major market downturns.
Implement systematic rules to exit or reduce exposure during unfavorable conditions.
Integrate the Macro Context into Systematic Strategies
While trading execution should remain systematic, macroeconomic awareness helps inform capital allocation.
Monitor inflation, interest rates, and credit markets to adjust portfolio exposure.
Allocate capital dynamically to different asset classes depending on macroeconomic trends.
Build a Systematic Trading Strategy Framework
Trend Following: Use moving averages or breakout levels to determine trend direction.
Momentum Ranking: Rank assets by relative strength and filter out underperformers.
Volatility Adjustments: Ensure assets provide sufficient returns to justify their risk.
Customize factor models for different asset classes to optimize performance.
Managing Market Toppiness and Volatility
Monitor breadth indicators to detect declining market participation.
Be cautious when major indices are unable to confirm new highs.
Adjust exposure dynamically as market volatility increases.
Use systematic trend-following rules to avoid exposure to deteriorating markets.
Be Mindful of Asset-Class Volatility
Avoid applying identical rules to all asset classes—adjust for their unique volatility and behavior.
Rank assets based on their volatility-adjusted returns rather than absolute performance.
Use normalized risk-adjusted ranking to ensure fair comparisons between asset classes.
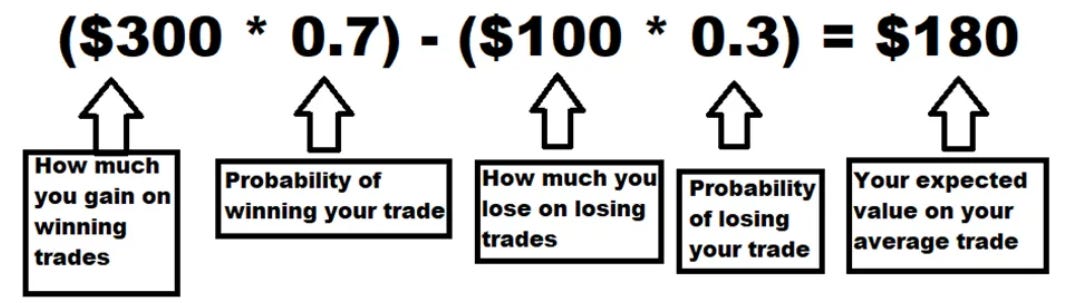
Understanding the Importance of Mathematical Expectancy
View trading as a probability-based business similar to casinos and insurance companies.
Calculate expectancy using the formula:
(Source: Steady Options)
Favor strategies with consistent positive expectancy rather than relying on occasional large wins.
Use expectancy as a measure of strategy robustness before deploying capital.
Hope you enjoyed this newsletter, see you next week!
(This newsletter is not investment advice, all views are my own.)